Fetal Surgery
Fetal surgery is a branch of the fetal maternal medicine subspecialty, which has several surgical techniques used for the in-utero treatment of congenital defects of the fetus.
There are 3 types of procedures:
1.
Microneurosurgery
This procedure is used in fetuses with open spina bifida (myelomeningocele), it is minimally invasive, because it is done in the uterus, away from the placental insertion with a maximum diameter of 3-4cms between 19 to 27 weeks of gestation. The purpose of this intervention is the baby's ability to walk, diminish the need of a ventriculoperitoneal valve due to hydrocephalus and correct the cerebellar and cisterna magna compression (Arnold Chiari II), allowing a better prognosis for motor and neurological skills as well as a better quality of life.
2.
Fetoscopy
This is also a minimally invasive surgery, it is done via a small incision through the maternal abdomen with a fetoscope with fiber optic illumination (similar to endoscopy), allows the direct visualization of the fetus, placenta and umbilical cord simultaneously using ultrasound technology.
3.
Percutaneous Procedures
A catheter is placed, which allows to monitor the fetus via guided ultrasound.
The following diseases or defects are candidates for fetal surgery:
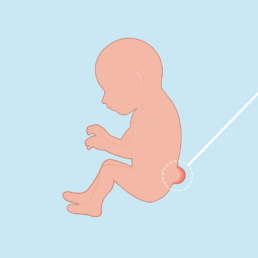
Myelomeningocele (open spina bifida)
A birth defect that occurs when the spine of the baby does not correctly close during pregnancy. The ideal treatment consists of corrective surgery inside the womb.
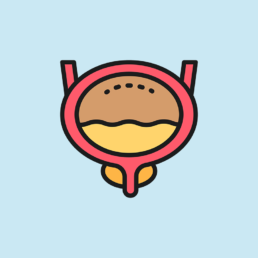
Low urinary tract obstruction (LUTO)
It is a malformation of the male fetuses, in which there is a total obstruction of the urethra at the level of the bladder, that can be due to urethral posterior valves or urethral stenosis.
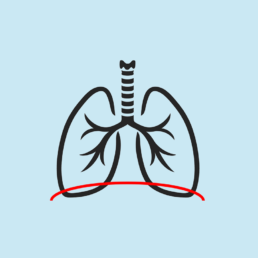
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
A birth defect, where the diaphragm (the muscle that separates the thorax from the abdomen) has an orifice. The organs of the abdomen, like the intestines, stomach, and/or liver can be displaced through this orifice into the thoracic cavity and compress the lungs and heart. If the baby's lungs are small and not fully developed at birth, he/she can die from an underdevelopment of the lungs. In this surgery, a balloon is placed on the trachea of the fetus, which allows the lungs to expand and develop in a better way, thus increasing the chances of the baby's survival.
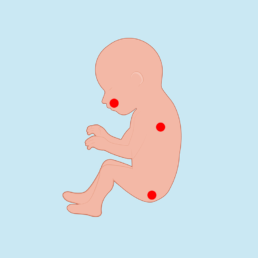
Fetal tumors
It is a procedure done through laser ablation of the tumor's feeding vessel, that permits the growth of the mass.
Amniotic bands
These are destroyed through laser and fetoscopy to decrease the risk of amputation of the affected part.
Twin-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) or selective growth restriction (sIUGR)
This condition allows one twin to receive more blood causing an overload and the donor co-twin having less blood thus leading to anemia. If the circulation (vessels) is not separated this could lead to the demise of both twins. It is treated by laser coagulation of the blood vessels shared in the placenta by both twins.
Pulmonary masses (pulmonary sequestration, cystic adenomatous malformation)
Different treatments can be done in these cases, like the placement of a shunt or toracoamniotic drainage, laser ablation (to stop the blood supply from the feeding vessel to reduce the tumor) or sclerotherapy.
Congenital high airway obstruction syndrome (CHAOS)
In severe cases and those where there is no spontaneous remission, if a membrane is present, this can be destroyed by laser ablation or an EXIT surgery can be done.
